What is an ISO Container and How is it Used in Shipping?
ISO containers have revolutionized the shipping industry. These standardized boxes come in various sizes and designs. They provide a safe way to transport goods globally. The term "ISO" stands for International Organization for Standardization. This ensures that containers can fit on different transport modes, like ships and trucks.
ISO containers are built for durability. They withstand harsh weather and rough handling. This makes them ideal for long journeys across oceans. Additionally, containers are easy to stack. This maximizes space on cargo ships. However, one must consider the cost of maintaining and managing these containers.
Not everyone realizes the complexity involved in using ISO containers. Issues like corrosion and wear can arise over time. Moreover, not all goods fit well into these containers. So, careful planning is essential. Understanding the intricacies of ISO containers can help optimize shipping logistics. Even small mistakes can lead to delays. Thus, attention to detail is crucial in marine transport.
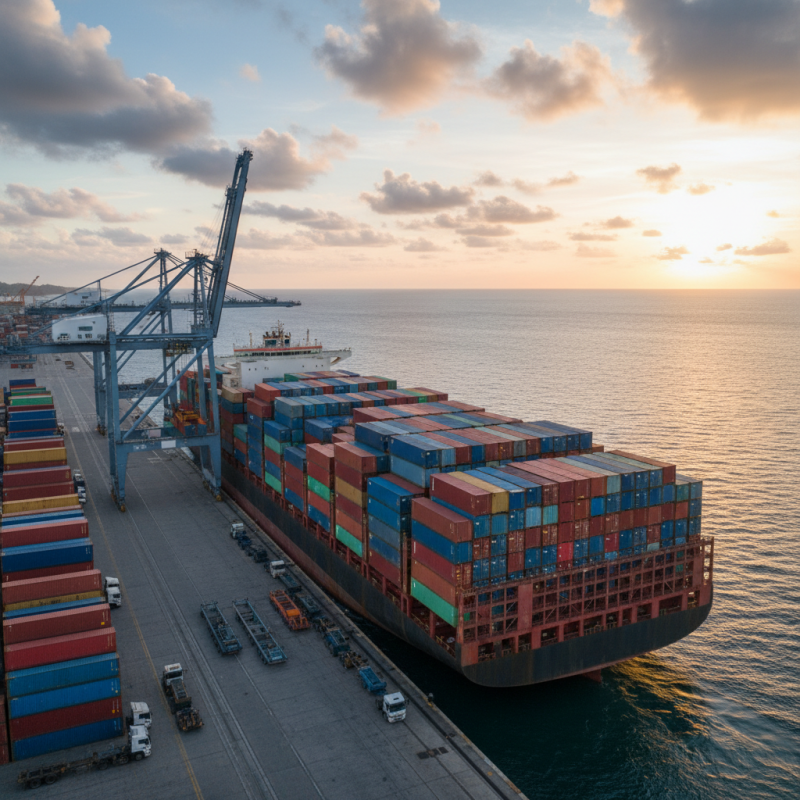

What is an ISO Container?

An ISO container, often known simply as a shipping container, is a standardized unit used for transporting goods. These containers are usually made of steel. They come in various sizes, typically 20 or 40 feet long. This standardization allows them to fit seamlessly on trucks, ships, and trains.
ISO containers protect cargo during transport. They are waterproof and secure, minimizing damage from environmental factors. Their design enables efficient stacking and storage. This helps save space in ports and on vessels. However, not all containers are in perfect condition. Some may have dents or signs of wear. This can affect how they protect the cargo inside.
In recent years, the demand for ISO containers has surged. Many companies opt for these containers due to their versatility. They can move anything, from electronics to textiles. Yet, challenges remain in maintaining and managing the containers. Improper handling can lead to loss of cargo integrity. Additionally, the environmental impact of shipping cannot be overlooked. It's essential to reflect on sustainable practices in this industry.
History and Development of ISO Containers
The history of ISO containers dates back to the 1950s. Malcolm McLean, an American businessman, revolutionized shipping with his containerization concept. He believed that standardizing cargo would improve efficiency. In 1961, the International Organization for Standardization established the first ISO standards. This standardization allowed containers to fit on various transport modes seamlessly.
As of 2020, the number of shipping containers in circulation reached around 40 million. This figure reflects the booming demand for global trade. However, not all containers meet modern specifications. About 15% of containers are not compliant with ISO standards. This non-compliance causes challenges in international logistics. Proper regulations are essential to maintaining safety and operational efficiency.
Over the decades, the shipping industry has adapted containers for diverse uses. Today, you’ll find refrigerated containers and tank containers among regular box types. The expansion of these designs highlights ongoing innovation. Yet, the industry also faces environmental concerns. The rise of e-commerce boosts container usage, while emissions continue to rise. Balancing growth with sustainability is a pressing issue.
Growth of ISO Container Usage Over the Years
This chart illustrates the growth in the number of ISO containers shipped over the years, highlighting the increasing reliance on standardized containers in global shipping. The data shows a steady rise in usage from 2000 to 2023, reflecting the adaptation of shipping practices worldwide.
Types of ISO Containers Used in Shipping
ISO containers, also known as intermodal containers, are essential in shipping. They come in various types, each designed for specific cargo needs. The standard dry container is the most common, suitable for non-perishable goods. Typically, these containers are 20 or 40 feet long and offer a secure way to transport items around the globe.
There are also refrigerated containers. These keep perishable goods at a stable temperature. They are crucial for shipping food and pharmaceuticals. Bulk containers are another type, designed for transporting loose materials. These are commonly used for agricultural products like grains and seeds.
Specialized containers exist as well. Tank containers transport liquids safely, while open-top containers accommodate oversized cargo. Each type of ISO container serves a purpose. However, not every container type is suitable for all shipments. It requires careful planning to select the right container, as poor choices may lead to cargo damage or increased costs.
Applications of ISO Containers in Global Trade
ISO containers play a vital role in global trade. They facilitate the shipping of goods across oceans and continents. According to industry reports, over 90% of international trade is carried by sea, mostly using ISO containers. These standardized metal boxes enhance efficiency, safety, and security in cargo transport.
Various industries utilize ISO containers. Agricultural products, electronics, and machinery often travel in these units. The flexibility of ISO containers allows for easy stacking and efficient use of space on ships and trucks. This maximizes shipping capacity.
However, not all shipments are hassle-free. Issues like container damage or delays can disrupt supply chains. According to the World Shipping Council, more than 600,000 containers are estimated to be lost at sea every year. This raises concerns about insurance and loss mitigation strategies.
Sustainability is another challenge. As the industry grows, so does the environmental footprint of shipping. ISO container manufacturing and transport contribute to carbon emissions. Adopting eco-friendly practices in logistics is critical. Some shipping companies are exploring greener alternatives, but the path is still fraught with hurdles. Finding the balance between efficiency and sustainability will shape the future of global trade.
Benefits of Using ISO Containers for Shipping Logistics
ISO containers are crucial in modern shipping logistics. These standardized units simplify the process of transporting goods. They promote efficiency across various transportation modes, including ships, trucks, and trains. According to the International Maritime Organization, over 90% of global trade is carried by sea, with ISO containers playing a significant role in this movement.
Using ISO containers offers significant benefits. They enhance safety and security during transportation. The structure of these containers protects goods from damage. A report by the World Shipping Council states that containerized shipping reduces cargo loss rates by up to 90%. This is vital for high-value shipments. However, improper packing remains an issue. It can lead to damage and inefficiencies.
Another advantage is their versatility. ISO containers come in various sizes and materials. They accommodate different types of cargo, from perishable goods to machinery. The flexibility helps businesses adapt to changing needs. Yet, there are still challenges. Sustainability is a concern, as many containers are made from new materials. This raises questions about environmental impact and resource use. The industry must continually innovate to address such issues.
Related Posts
-
What is an 8ft Shipping Container and How Can It Benefit Your Business
-

20 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right 20ft Storage Container
-

2025 Top 10ft Storage Container Options for Your Storage Needs
-

Best 10x10 Storage Container Options for Maximum Space Utilization
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using ISO Containers for Your Shipping Needs
-

Why Choose a 10x10 Storage Container for Your Needs?
